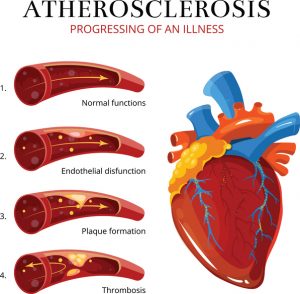
 Atherosclerosis is the condition in which the arteries become hardened, preventing a healthy flow of oxygenated blood. This process is common in aging, as plaques can build up causing arteries to become stiff. Plaque buildup also makes the arteries narrow, this way limiting the blood flow as well.
Atherosclerosis is the condition in which the arteries become hardened, preventing a healthy flow of oxygenated blood. This process is common in aging, as plaques can build up causing arteries to become stiff. Plaque buildup also makes the arteries narrow, this way limiting the blood flow as well.
Atherosclerosis is a dangerous condition because it increases the risk of a heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Although arthrosclerosis is often associated with age, it actually occurs much earlier than you may think. This condition can begin as early as your 20s, and by 30s these changes start surfacing. Although routine checks may come back normal, after the age of 40 issues like cholesterol become evident. For men, signs of atherosclerosis can be seen as early as the age of 45, and for women, it’s around the age of 55.
Advertisement
Let’s take a look at some preventative measures you can take in order to reduce your risk of atherosclerosis and the associated complications.
Dietary Guidelines for Atherosclerosis
The main culprit behind atherosclerosis is plaque buildup, which is a result of cholesterol. Hence, it is important that you eat foods that are not only healthy but help lower your LDL cholesterol and boost HDL cholesterol. Making changes to your diet in order to prevent or slow the progression of atherosclerosis can also help to keep your cholesterol levels in check. Because high cholesterol levels can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, the same lifestyle modifications you apply to prevent your cholesterol levels from becoming too high can also be used towards preventing atherosclerosis.
There are four main guidelines when it comes to atherosclerosis prevention through diet:
- Choosing plant-based foods like fruits and vegetables
- Minimizing refined grains, added salts, and sugars
- Including nuts and seeds into your diet, avoiding most oils
- Avoiding foods containing saturated or trans fats
One of the most important diet changes to make is to minimize the intake of refined sugars. Cakes, candies, and other high-sugar foods can raise triglycerides and lower HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol). Both of these could promote the formation of atherosclerosis in the body.
Another important change in diet to keep in mind is making sure to only consume a moderate to low consumption of alcohol. It should be no more than two glasses of alcohol for men and only one glass for women a day to help lower the risk of heart disease.
You will also want to reduce the amount of saturated fat and avoid foods containing trans fats entirely. Trans fats are found in processed foods like chips and cookies. Instead, try snacking on foods that are higher in unsaturated fat such as nuts and olives.
A heart-healthy diet includes low-fat dairy products, fresh fruits and vegetables, skinless poultry and fish, and non-tropical vegetable oils. Studies show that many chemicals found in these foods, including phytosterols and polyphenols, can help to lower lipids and possibly reduce inflammation.
Including herbs into your diet is another great way to help prevent and treat plaque buildup in the arteries. Studies show that garlic is a great way to lower cholesterol levels, prevent blood clots and destroy plaque. It works by reducing the “stickiness” of blood platelets. This is due to the main active ingredient in garlic called allicin and the constituent ajoene.
According to studies cited by the University of Michigan Health System, garlic might be most beneficial to women in treating and preventing atherosclerosis. Although fresh garlic is effective, aged garlic extract could help to prevent oxidation of LDL cholesterol which can prevent the development of atherosclerosis and plaque buildup in the arteries. The University of Maryland recommends taking 900 mg per day of garlic powder supplements that are standardized to contain 0.6 percent allicin.
Another herb known to reduce platelet stickiness and help clear arteries of plaque is ginger. Consuming either fresh or dry ginger can affect blood platelets, but the University of Michigan Health System recommends taking at least 10 g, or 1 heaping tsp. to achieve the benefits. Ginger contains more than 12 antioxidants which can improve circulation and lower the risk of blood clots.
Exercise and Physical Activity for Atherosclerosis
 A study published in the American College of Sports Medicine found that regular physical activity of large muscle groups such as those involved walking, running, or swimming, can reduce symptoms associated with coronary artery disease, which can result from atherosclerosis. Regular exercise is well documented to help reduce cholesterol, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce your risk of other conditions such as diabetes that can contribute to atherosclerosis.
A study published in the American College of Sports Medicine found that regular physical activity of large muscle groups such as those involved walking, running, or swimming, can reduce symptoms associated with coronary artery disease, which can result from atherosclerosis. Regular exercise is well documented to help reduce cholesterol, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce your risk of other conditions such as diabetes that can contribute to atherosclerosis.
The study found that regular physical activity was associated with a reduction of many risk factors contributing to atherosclerosis. The study was a meta-analysis of 52 training trials involving of 4,700 participants over the course of 12 weeks. HDL cholesterol was found to improve and LDL cholesterol was reduced.
The studies also revealed a reduction in blood pressure as a result of regular exercise, along with a reduction in insulin resistance.
As you can see, it is not only important to eat a healthy diet in order to reduce the risk factors associated with atherosclerosis, but combining it with regular physical activity can help support healthy arteries and maintain overall good health.
Other Treatment Options for Atherosclerosis
There are three main types of treatment options when it comes to atherosclerosis: lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery.
Because many lifestyle habits contribute to hardening of the arteries, addressing these can help improve the condition. This involves eating healthy, reducing sodium and saturated and trans fats in your diet, not smoking, and exercising regularly.
Prescribed medication works to lower blood pressure and cholesterol, and even prevent blood clots (known as antiplatelets).
Lastly, surgery can be used to open up and widen the arteries in order to address the blockage.
Research shows that 90 percent of heart attacks are due to the following risk factors:
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Excessive consumption of alcohol
- Sedentary behavior
- Stress
- Insufficient intake of fruits and vegetables
Advertisement
By controlling these risk factors, you can better reduce your risk of atherosclerosis or even reduce your risk of the associated complications. You should also know your family health history, especially if you have parents or other close relatives that developed cardiovascular disease or high cholesterol levels early in life. This can help your health practitioner put together a risk assessment for you and offer an insight to what changes you may benefit from the most.
Along with prevention, it is also possible to reverse atherosclerosis to some degree. However, it is a long process and it doesn’t undo itself that quickly. It takes time and serious commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle. But by keeping your weight, cholesterol, and blood sugars within normal ranges, you can help to reduce plaque formation in your vessels.
Depending on your risk factors and current condition, your doctor will recommend the best treatment, which will often combine lifestyle factors with medical intervention.
