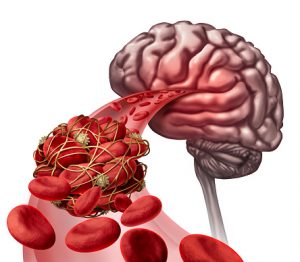
A blood clot forms in an attempt to repair some sort of damage to a blood vessel. It is a gel-like mass that is formed by platelets and fibrin (a protein involved in blood clotting) to help stop bleeding. When blood clots form the wrong way inside an artery or vein, it can cause serious problems. People who smoke, take birth control pills, and are sedentary are at a higher risk of getting blood clots.
What are blood clots?
Usually, blood flows freely through our veins and arteries. A certain level of blood clotting is normal and necessary to stop us from bleeding when we get injured. However, complications occur when there is too much clotting. There are two different types of blood clots.
Arterial clots form in the arteries and cause immediate symptoms. This is due to the fact that the clot prevents oxygen from reaching vital organs. This can lead to stroke, heart attack, and even paralysis. Venous clots form in the veins and develop slowly over a long period of time. Symptoms may be mild and then become more noticeable as time passes.
Blood clots can occur in different parts of the body. For example, they can happen in the arms and legs. In these cases, cramping, swelling, and tenderness are likely. Clots can also happen in the heart and involve pain in the chest and left arm, as well as sweating and difficulty breathing. Lungs are also an area of the body that can be prone to blood clots. If a person has a clot in the lung they might have a hard time breathing, they will likely cough a lot and experience chest pain.
Abdominal clots are also possible and come with severe stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. When it comes to blood clots in the brain, there are many potential signs, including problems with vision or speech, seizures, and a feeling of weakness or fatigue. Depending on where the blood clot is, the situation can be life-threatening.
Blood clots in the brain: Causes
There are many reasons a person may have a clot in the brain. Here we take a detailed look at the causes of blood clots in the brain:
Head injuries. If there is a serious injury or trauma to the head and/or neck, the body will form a clot to stop the bleeding. This can put a lot of pressure on surrounding brain tissue. Some traumas can cause blood clots to form outside the brain and break loose. These have the potential to become lodged in the brain and cause a stroke.
Narrowing or hardening arteries. When arteries harden or narrow the risk of developing a clot in the brain increases. Hardened arteries can tear as they pump blood, which can lead to a clot forming. These clots can cut blood flow off to the narrowed artery, causing serious damage to surrounding cells.
Travelling clots. Some clots will travel from one part of the body to a blood vessel that leads to the brain, causing a blockage, which can result in a stroke or cerebral embolism. These clots can cause damage to other parts of the body before they reach the brain.
Inflammation. If a superficial vein is overinflamed it can lead to an increased risk of blood clots. An injury or bacterial infection can cause inflammation. This can reduce blood flow and damaged areas will be at risk of leaking, which can lead to blood clots.
Blood clots in the brain: Signs and symptoms
When someone has a blood clot in the brain, they could experience a variety of different symptoms. For some people, it starts with headaches, but it progresses to a wide range of other signs, such as difficulty speaking and even depression.
The following covers the main symptoms of blood clots in the brain:
- Headaches – They are normally felt on one side of the head and can be made worse by coughing or sneezing. For some people, headaches linked to blood clots can make head movement and physical activity hard.
- Speech difficulties – Some people might begin to slur words or have other difficulties with speaking. This is more common when a person has a clot on the left side of the brain.
- Confusion – It can take longer to think or understand something.
- Dizziness – Periods of dizziness can happen and may be accompanied by temporary blindness.
- Changes in personality – You can feel suddenly manic or suddenly subdued.
- Depression – This can happen when the brain isn’t getting the right amount of oxygen.
- Loss of coordination – Some people find they are unable to move with the same level of coordination, and the ability to move an object from one hand to the other may be especially affected.
- Seizures – There are those with blood clots in the brain that experience seizures lasting up to two minutes.
- Ischemic attack – Also called a “mini stroke”, this can cause dysfunction on one side of the body and has the potential to turn into a full-blown stroke.
- Paralysis – One side of the body may become paralyzed. The arm, leg, and face are particularly affected.
Blood clots in the brain: Treatment options
If a blood clot is suspected, medical attention is crucial. An MRI or CT scan may be used to diagnose a clot and, perhaps, the condition that caused it. Anticoagulants such as aspirin can be used to help dissolve blood clots. Sometimes blood clot patients take aspirin on a regular basis to prevent the development of new clots. There are also situations where surgery is necessary. Yes, a blood clot can be removed from the brain. Arteries can also be opened up and scraped clean to reduce the risk of injury.
People who are at risk of getting more clots may have what is called a “plasminogen activator” inserted in a vein. This releases a clot-busting drug right into the brain to prevent a stroke from happening.
The idea of blood clots in the brain does sound rather frightening. If you experience a severe and sudden headache, difficulty speaking, or difficulty seeing, this may or may not be a sign of a blood clot. No matter what the cause, you should seek medical attention immediately. The sooner these types of symptoms are looked at, the quicker treatment can be administered and the more likely you will have a positive outcome.
It is important to note that despite what many people think, blood clots are not just something that happens to elderly, it can happen to young people too. Lack of awareness about blood clots can cost lives, so the more you educate yourself about clots, the better.