 End stage renal disease (ESRD) is the last stage of kidney disease (stage 5) in which the kidneys cannot function any longer are unable to keep up with the daily needs of the body. At this stage, dialysis or a kidney transplant is necessary in order to treat the disease.
End stage renal disease (ESRD) is the last stage of kidney disease (stage 5) in which the kidneys cannot function any longer are unable to keep up with the daily needs of the body. At this stage, dialysis or a kidney transplant is necessary in order to treat the disease.
The role of the kidneys is to filter waste from blood and urine. In kidney disease, the kidney’s ability to do this becomes impaired. With each passing stage, kidney function progressively decreases, so waste cannot be expelled and builds up in the body.
Advertisement
Those with end stage renal disease have kidney function below 10 percent, meaning the kidneys are barely functioning or not functioning at all.
Kidney function is measured by glomerular filtration rate (GFR). In stage 5, the kidneys’ GFR is less than 15. To compare, healthy GFR is above 90.
Prevalence of Stage 5 Kidney Disease
Over 660,000 Americans are treated for kidney failure annually. Men are more affected by kidney failure than women and it is most commonly seen in adults aged 45 to 64. White Americans are more likely to be diagnosed with stage 5 kidney disease and American Indians are diagnosed the least.
Stage 5 kidney disease: Causes, risk factors, and complications
Kidney disease develops when the kidneys become damaged and their function is impaired. There are many different reasons for this. For example, in diabetics, high levels of glucose circulating in the blood can put stress on the kidneys as it cannot be broken down or expelled, damaging the kidneys. Kidney disease is also more common in high blood pressure patients.
Other causes of kidney disease include a blockage of the urinary system such as kidney stones, inflammation of the filters to the kidneys, urine flowing into the kidneys – known as vesicoureteral reflux – and congenital defects.
Risk factors for kidney disease include diabetes, hypertension, family history of kidney disease, polycystic kidney disease, Alport syndrome, interstitial nephritis, kidney infection, and certain autoimmune conditions like lupus.
Complications resulting from ESRD include skin infections and dry skin, increased risk of infections, abnormal electrolyte levels, joint, bone and muscle pain, weak bones, nerve damage, changes in blood glucose levels, liver failure, heart and blood vessel problems, fluid buildup around the lungs, malnutrition, thyroid problems, anemia, stomach and intestinal bleeding, brain dysfunction and dementia, seizures, joint disorders, and fractures.
What are the symptoms of ESRD?
Symptoms of ESRD can vary greatly and can include:
- Decrease in urine output
- Inability to urinate
- Fatigue
- General feeling of illness
- Headache
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dry skin and itchiness
- Changes in skin color
- Bone pain
- Confusion
- Easy bruising
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Numbness in extremities
- Bad breath
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent hiccups
- Absence of menstrual cycles
- Sleeping problems
- Low libido
- Swelling of the legs or hands
ESRD or Stage 5 kidney disease diagnosis
ESRD is diagnosed through a series of tests to determine kidney function, including urinalysis, serum creatinine test, blood urea nitrogen test, and estimated glomerular filtration rate.
By combining the results of these tests, your doctor can determine how well your kidneys are functioning and determine the stage of your kidney disease. Poor results, especially low GRF, will indicate ESRD.
Once ESRD is diagnosed, your doctor will be monitoring you for some time to gauge your kidney condition at this point. It is rare that kidney disease is first initially diagnosed at the fifth stage.
Related: Renal diet: Foods to eat and avoid for kidney failure
Treating end stage renal disease or stage 5 kidney disease
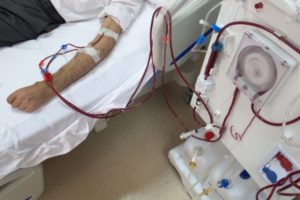
In ESRD, kidney function is barely available, so dialysis or a kidney transplant is highly recommended. In dialysis, patients are hooked up to a machine filtering the blood and waste as the kidneys are unable to do so on their own. Another form of dialysis is known as peritoneal dialysis in which a solution is placed into the abdomen and later removed with a catheter.
For a kidney transplant, the diseased kidneys are removed and a donated one is then put in its place. You only need one healthy kidney to function, so kidney donors are often living.
Medications are also advised for ESRD as a means to control and manage other conditions that can contribute to worsened outcomes of the disease – for example, drugs for controlling blood pressure or diabetes. On the same note, lifestyle changes should also be implemented in order to improve underlying conditions and kidney function. For example, a patient may have to change their diet to ensure there is less waste being produced. They may also need to consume food that is easier for the kidneys to break down. Red meat is an example of a food that should be avoided as it is difficult for the kidneys to process. Reducing sodium and potassium is also advised as fluid levels can become unbalanced in kidney disease.
End Stage Renal Disease Diet
Patients with end-stage renal disease need to follow a specific diet as to not worsen their condition. Not only does this diet ensure kidney health doesn’t worsen, but it can also prepare patients for a kidney transplant. Furthermore, the key to this diet is to reduce complications linked to uremia, which is when waste accumulates in the bloodstream and can lead to malnutrition.
There are five key components to stage 5 renal disease diet. It includes:
Know how much protein to consume each day and stick to that: Limiting protein can help control uremia. On the other hand, too little protein can contribute to malnutrition. Recommended protein intake is 0.6 to 0.75 grams of protein per kilogram of bodyweight. A registered dietician can help you achieve the appropriate protein intake.
Eat enough calories to maintain weight, even if you are overweight: There are many different reasons why stage 5 kidney disease patients don’t consume enough calories such as gastrointestinal problems, depression, food intolerances, medications, and other medical conditions. It’s important that patients maintain their weight as it helps maintain their muscle.
Monitor potassium levels: When the kidneys don’t function properly then potassium can build up. It’s important that you monitor your potassium intake as to not allow for potassium accumulation. High potassium foods include: avocado, bananas, cantaloupe and honeydew, dried fruit, legumes, milk and yogurt, nuts and seeds, oranges and orange juice, potatoes, pumpkin and winter squash, salt substitutes and low sodium foods that may contain potassium additives, and tomato products.
Watch your phosphorus levels: When limiting protein, it is natural for phosphorus levels to change, too, as the go together. To increase phosphorus levels are to consume foods with phosphorus additives.
Control fluid retention and blood pressure with low sodium and medications: It’s important that you monitor your weight daily to watch for any fluid weight gains which can lead to swelling and shortness of breath. A high sodium diet can cause fluid retention, so consuming less sodium can help prevent fluid retention. Your doctor and dietician can help with recommendations of sodium intake.
ESRD Recovery
Recovery is largely based on treatment. Patients on dialysis have a prolonged life because their blood is being filtered. For some patients, they can complete dialysis at home instead of visiting a clinic. This allows for more personal freedom.
Kidney transplants also have a high succession with failures of a transplant being quite low. A kidney transplant allows for a person to go back to living a normal life. As long as a patient continues to live healthy, they will reduce their risk of future kidney disease.
Prevention, Prognosis of Stage 5 Kidney Disease
As medicine advances, so does the improvement of prognosis of stage 5 kidney disease. Prevention is highly important as to not progress kidney disease. This can be done mainly by adhering to a healthy lifestyle that includes losing weight if necessary, being active, eating a balanced diet that is low in sodium, controlling your blood pressure, taking medications as prescribed, control blood sugar levels, don’t smoke or use tobacco products, and get regular check-ups.
Prognosis has vastly improved for kidney disease patients as long as they receive treatment. By properly managing kidney disease along with other medical conditions, a patient with kidney disease can have a long life, especially if a kidney transplant is available.
Tips for Stage 5 Kidney Disease Patients
It may not be easy to hear that you have stage 5 kidney disease and facing such a diagnosis alone can cause more harm than good. It’s important that you find healthy ways to cope with your diagnosis along with having a good support group around you to ensure you continue on with your treatment.
Advertisement
Here are some coping tips to help you get through:
- Connect with others with kidney disease as they understand what you’re going through.
- Maintain normal routines as much as possible. This can help cope with negative emotions and help you feel as normal as you can.
- Be active on most days: Try to get at least 30 minutes of activity a day as it helps improve mood along with fatigue and stress.
- Open up to someone you trust because bottling up your feelings and emotions will only make you feel worse.
Living with stage 5 kidney disease isn’t easy, but there is hope with a good support system and proper medical treatments.
Related: Renal colic: Symptoms, causes, and prevention tips
