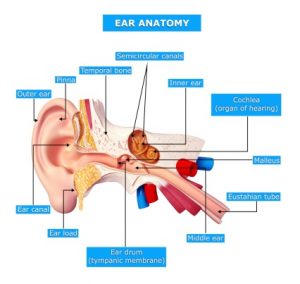
 Eustachian tube dysfunction affects the small tube that connects the back of the nose with the middle ear. This tube allows air to travel to the eardrum, as well as lets mucus drain from the middle ear, so that pressure on either side of the eardrum is maintained and sound can be properly transferred to the brain. When this tube functions incorrectly, it can impair your ability to hear, resulting in a condition known as Eustachian tube dysfunction, or ETD.
Eustachian tube dysfunction affects the small tube that connects the back of the nose with the middle ear. This tube allows air to travel to the eardrum, as well as lets mucus drain from the middle ear, so that pressure on either side of the eardrum is maintained and sound can be properly transferred to the brain. When this tube functions incorrectly, it can impair your ability to hear, resulting in a condition known as Eustachian tube dysfunction, or ETD.
What is Eustachian tube dysfunction?
When the eustachian tube becomes blocked or fails to open, air pressure within the ear can build up and press on the eardrum. This prevents the eardrum from vibrating properly and impairs your ability to hear. Your hearing may become dull and muffled, and you may experience some pain and hear a popping or clicking sound. ETD is often accompanied by the symptoms of a common cold or flu.
Can flying cause Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Advertisement
Those with existing Eustachian tube issues may experience the symptoms of ETD when flying due to the significant changes in cabin air pressure. Eustachian tube dysfunction can make it difficult for your ears to adapt to these changes, especially during the descent of the aircraft. Negative pressure develops within the ear that tends to lock the Eustachian tube closed, though this discomfort may be relieved by yawning, swallowing, chewing, or “popping” your ears.
Eustachian tube dysfunction: Symptoms
The most common symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction are muffled hearing, pain, ringing or buzzing in the ear, and dizziness. These symptoms may also be accompanied by those of the common cold and can last anywhere between a few hours and several weeks.
What causes Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Eustachian tube dysfunction can be a result of multiple conditions and/or complications, such as an ear infection. Other causes include:
Allergies. Allergies that cause excess mucus to be produced can also cause inflammation throughout the entire sinus system. Hay fever and perennial rhinitis are the allergies most commonly associated with this issue, as the additional mucus produced by these conditions can drain into the Eustachian tube and cause it to become plugged or feel full.
Glue ear. This condition causes the middle ear to fill with a sticky, glue-like fluid that leaks into the Eustachian tube, creating a blockage that prevents proper air flow in and out of the ear. This results in a tightening of the eardrum that worsens if the fluid sticks to the drum itself and impairs your ability to hear.
Blockages. A blockage can occur due to an enlarged adenoid or, in some cases, a tumor in the back of the nose that pushes against the Eustachian tube, causing it to close and become blocked.
Smoke. Regular exposure to smoke can damage the small hairs in the ear known as cilia, impairing your body’s ability to drain the middle ear through the Eustachian tube.
Altitude changes. Quickly moving to a different altitude, whether through air travel, diving, and even some elevators can result in your Eustachian tube feeling restricted.
Eustachian tube dysfunction treatment
If the discomfort you experience due to your Eustachian tube dysfunction is severe, you may require medical or surgical treatment. These treatments include the use of allergy medication and nasal decongestants, provided the cause of your discomfort is irritation due to allergies. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to restore hearing and relieve pressure. The two most common operations are:
Myringotomy. In this procedure, a small incision is made into the eardrum and any fluid inside can be suctioned out. The incision is usually left open long enough for the Eustachian tube to heal so that when the eardrum heals after approximately three days, the pressure and fluid do not re-accumulate.
Pressure equalization tubes. Following a myringotomy, a small hollow tube is inserted into the eardrum to help provide proper ventilation to the middle ear for approximately six to 12 months. As the eardrum heals, the tubes are pushed out naturally and do not usually need to be replaced unless the condition is chronic.
Eustachian tube dysfunction: Natural treatment
If your condition is not severe, Eustachian tube dysfunction may be treated with home remedies, though if you feel the discomfort worsening, it is best to contact your doctor. Home remedies include:
Leave it be. If you know the cause of your ETD is either a cold or altitude change that is putting pressure on your ears, you can leave your symptoms to resolve on their own as these blockages often go away within a week.
Chew and swallow. These actions cause the Eustachian tube to open and close, aiding in the draining of the middle ear and providing relief.
Advertisement
Self-inflation. Take a deep breath, keep your mouth closed, and pinch your nose shut, then blow out gently without opening your nose or mouth. This can inflate the Eustachian tubes and relieve pressure, though it should be done carefully as it can also cause damage to the eardrum.
Plugged ears accompanied by muffled hearing, pain, dizziness, and common cold symptoms may be due to a condition affecting the middle ear called Eustachian tube dysfunction. This issue may be caused by colds, altitude changes, smoke exposure, and even allergies, and in serious cases may be relieved by small surgical operations. Home remedies also exist to ease symptoms associated with this condition, however, if you feel that your ETD may be cause for concern, it is important to contact your doctor as it may be more severe than originally thought.
Related: Middle ear infection (otitis media) treatments at home
