 Heart valve disease refers to a group of conditions preventing the heart valves from properly functioning. It disrupts circulation and may turn into a life-threatening condition. When heart valve disease is spotted early on, the function of the heart valve can be successfully restored with treatment.
Heart valve disease refers to a group of conditions preventing the heart valves from properly functioning. It disrupts circulation and may turn into a life-threatening condition. When heart valve disease is spotted early on, the function of the heart valve can be successfully restored with treatment.
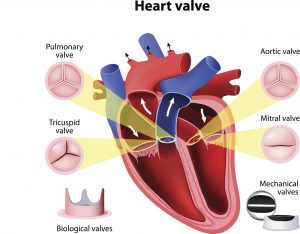
The heart has four main valves, known as the mitral, tricuspid, aortic, and pulmonic. The role of the heart valves is to ensure blood flows in only one direction through the heart. To release blood, small flaps of tissue – leaflets – open and close, letting the blood in and also preventing the blood from flowing backwards. A condition affecting any of the valves or the leaflets is then known as heart valve disease.
Causes of heart valve disease
Advertisement
Advanced high blood pressure and heart failure: This can lead to heart enlargement or enlargement of the main arteries.
Atherosclerosis in the aorta: The aorta walls thicken and harden as a result of plaque buildup, limiting the passage of blood through the artery.
Damage and scar tissue due to a heart attack: After a heart attack, scar tissue can form, which can disrupt the circulation of blood or make it more difficult for the heart to function properly.
Rheumatic fever: This is caused by untreated infections such as strep throat. When the bacteria reach the heart, the heart valves and the heart itself can get damaged while fighting off the infection.
Infections: Infections that travel through the blood stream can reach the heart and cause damage. This is known as infectious endocarditis.
Autoimmune disorders: In autoimmune conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks itself. An example of this would be lupus. Autoimmune diseases can also damage the heart and heart valves, leading to heart valve disease.
Diet medicines: Fenfluramine and phentermine have been linked to heart valve problems.
Marfan syndrome: This is a congenital disorder affecting connective tissue.
Metabolic disorders: This is a cluster of conditions that can raise your risk for heart problems or diabetes. These include high blood pressure, insulin resistance, and being overweight.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy to the chest can contribute to heart valve disease.
Risk factors for heart valve disease
Advertisement
 Risk factors for heart valve disease include older age, a history of infectious endocarditis, rheumatic fever, heart attack, or heart failure, intravenous drug use, and risk factors for coronary artery disease (such as being overweight, smoking, having high blood pressure, not exercising, eating a poor diet, or having a history of heart disease).
Risk factors for heart valve disease include older age, a history of infectious endocarditis, rheumatic fever, heart attack, or heart failure, intravenous drug use, and risk factors for coronary artery disease (such as being overweight, smoking, having high blood pressure, not exercising, eating a poor diet, or having a history of heart disease).
In some cases, people are born with heart valve issues such as having two flaps instead of three in their aortic valve. Or, sometimes these flaps may fuse together and work as one. This increases the risk of heart valve disease as well.
Signs and symptoms of heart valve disease
To compensate for insufficient blood flow, your heart will have to work much harder. Symptoms that accompany this overworking of the heart include chest pain or palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness or loss of consciousness, quick weight gain, as well as swollen ankles, feet, or abdomen.
