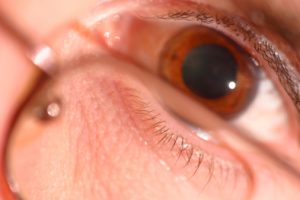
 Our eyes naturally constrict and expand in response to light that enters through them. On sunny days, pupils constrict or shrink to limit the amount of light that enters. When it is dark out, the pupils dilate to allow as much light in as possible. This shrinking and dilating are referred to as miosis and mydriasis respectively.
Our eyes naturally constrict and expand in response to light that enters through them. On sunny days, pupils constrict or shrink to limit the amount of light that enters. When it is dark out, the pupils dilate to allow as much light in as possible. This shrinking and dilating are referred to as miosis and mydriasis respectively.
The appearance of the eyes can be an important clue to diagnose various conditions affecting our health. How they respond to light can also be a telling sign.
Advertisement
A mydriasis definition can be expressed as having a blown pupil after sustaining a trauma or injury, sometimes resulting in unilateral mydriasis or bilateral mydriasis. Mydriasis can also be caused by problems with the nervous system.
What causes mydriasis?
Medicines: The following drugs have the added side effect of affecting pupil size:
- Atropine
- Antihistamines
- Pseudoephedrine
- Dimenhydrinate
- Amantadine (Symmetrel)
- Carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet)
- Anutruotykube (Elavil)
- Desipramine (Norpramin)
- Botulinum toxin (Botox)
- Phenobarbital (Luminal)
- Topiramate (Topamax)
Anticholinergics: A class of medication that blocks the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. It is often used to treat dizziness, vertigo, and motion sickness, but it can also be used for a variety of other medical conditions. Anticholinergic medication comes with certain side effects, including the dilation of your pupils, dry mouth, constipation, and decreased sweating.
Injury to the eye: Suffering from blunt force trauma to the eye may damage the nerves controlling the pupils or iris. This can interfere with normal functioning and cause them to appear blown out.
Increased oxytocin: The release of this hormone in high enough levels can lead to a temporary dilation of the pupils. Oxytocin is released by the posterior pituitary gland and plays a role in social bonding, sexual reproduction, and childbirth.
Drug use: Certain drugs such as cocaine, ecstasy, LSD, and crystal methamphetamine can lead to dilation of the pupils. The majority work by affecting the serotonin receptors in the brain, which can lead to mydriasis.
Cranial nerve neuropathy: This refers to gradual damage to the nerves of the eye, called the oculomotor nerve. This nerve is responsible for contraction and dilation, with damage to it affecting its ability to function properly. Cranial nerve neuropathy can affect one or both eyes with mydriasis, but can also result in impaired vision.
Traumatic brain injury: Sustaining blunt trauma to the brain can affect the eyes due to increasing levels of intracranial pressure. Both eyes may be affected.
Benign episodic unilateral mydriasis: Not related to any serious condition, but can sometimes affect women who get migraines. This condition can often cause mydriasis for several days, but it is possible to resolve only after a few hours, going back to normal.
Symptoms of mydriasis
Mydriasis symptoms will always involve widened or dilated pupils, and due to the fact that your pupils are required for normal vision, your sight is likely to be compromised to a certain degree as well. Depending on the etiology of your mydriasis, other symptoms may also present. The following are mydriasis symptoms you may encounter:
- Ptosis
- Blurred vision
- Eye irritation
- Dry eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Conjunctivitis (pink eye)
- Dizziness
- Ocular hypertension (increased pressure within the eye)
- Glaring of the eyes
- Night sweats
- Sleeping problems
- Weakness or pain in their lower back
- Retinitis which is inflammation of the retina in their eye
- Headaches
Treating mydriasis
Considering that there are a multitude of mydriasis causes, narrowing down its cause in your case is very important. Most treatment is tailored to help preserve eye function until the condition has resolved. This is typically done with an eye patch in cases of severe eye trauma. Head trauma will require emergency medical care.
Mydriasis due to drug or chemical exposure can be reversed almost immediately. However, most of the time, medical professionals will simply wait until the drug has worn off. There are safe medications that are used by doctors to purposely widen the pupils during eye examinations.
If mydriasis is not due to an underlying condition, it may be reversed using the following mediation.
- Phenylephrine drops
- Pilocarpine
- Steroids
- Atropine
- Scopolamine
How to manage mydriasis
Advertisement
It is important to recognize the cause of your dilated pupil as it will dictate the type of treatment most suitable. If it was simply due medication use, waiting for the drug to wear off should bring your pupils back to normal. It is recommended to avoid these medications in the future if possible and to switch to an alternative if the medication was required for health reasons.
Dilated eyes will be more sensitive to light than usual, so it is recommended to avoid bright places and to wear sunglasses when going outside during the daytime. It is not recommended to drive with dilated pupils as they may affect your vision.
It is important to remember that in most cases, mydriasis is often benign and temporary. The condition will usually go away on its own. If it doesn’t, it is recommended to seek professional medical assistance as soon as possible to get a more definitive diagnosis.
