
A painful lump behind the ear can be caused due to an abscess, a collection of pus developed when tissues or cells are infected by bacteria or mastoiditis, a bacterial infection that affects the mastoid bone or swollen lymph nodes behind the ear.
Here we will outline the five most common types, symptoms, and treatments for painful lump behind the ear.
Abscess behind ear
An abscess is a collection of pus typically caused by a bacterial infection. An abscess can occur in any part of the body, including behind the ear. There are two main types of abscesses: skin abscesses and internal abscesses.
A skin abscess develops beneath the skin and an internal abscess develops inside the body, in an organ or between organs.
When bacteria enter the body, white blood cells work to destroy them. As a means of fighting off the infection, parts of the surrounding tissue die creating a hole that can fill up with pus – this collection of pus is the abscess.
Symptoms and Causes of Painful Abscess
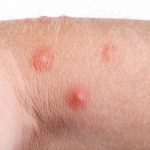
The main symptom of abscess is a painful, compressible mass, which is red, warm to touch, and tender. Some abscesses can rupture, some can progressively worsen without proper care, and complications can arise if the bacteria spread and infect other tissues.
How to treat abscess
Some abscesses may drain on their own, dry up, or shrink. But if abscess is large, antibiotics are required to treat the infection, and a doctor or surgeon may have to drain it by inserting a needle or making a small incision to cut the abscess open.
Mastoiditis Pain
Mastoiditis is a bacterial infection of the mastoid bone, which is located behind the ear and helps drain the middle ear. Inflammation or infection of the mastoid as a result of a middle ear infection can cause mastoiditis, and in some cases the infection can spread causing other complications.
Mastoiditis symptoms and causes
As mentioned, the cause of mastoiditis is a middle ear infection or bacterial infection that infects and inflames the mastoid.
Symptoms of mastoiditis include fever, irritability, lethargy, swelling of the ear lobe, redness and tenderness behind the ear, drainage from the ear, and bulging and dropping of the ear.
Mastoiditis treatment
Swollen lymph nodes
Swollen lymph nodes occur due to exposure to bacteria or viruses. Lymph nodes play a role in the body’s ability to fight off illness. Often swollen lymph nodes can resolve on their own, but if caused by an infection then treatment will be required to fight it off.
Swollen lymph nodes symptoms and causes
Swollen lymph nodes are caused by bacterial and viral conditions, including strep throat, measles, ear infections, abscessed tooth, mononucleosis, HIV, tuberculosis, certain sexually transmitted diseases, toxoplasmosis, infection from a cat scratch, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and some cancers, including lymphoma and leukemia.
Symptoms of swollen lymph nodes include runny nose, sore throat, fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, night sweats, as well as swollen, limb, hardened, fixed, rapidly growing lymph nodes. You should see a doctor if the swollen lymph node appeared without reason, if it is progressively growing over the course of weeks, if they don’t move if you touch them, you have a persistent fever or night sweats, and if swallowing or breathing becomes difficult.
Swollen lymph node treatment
Treatment of swollen lymph nodes can range from over-the-counter medications, heat applications, antibiotics and antiviral medications to local abscess drainage, as well as cancer treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation. If an immune disorder is the cause, the treatment should address it.
Acne behind ear
Acne symptoms and causes
There are many theories with regards to the possible causes of acne, including changes in hormones – which would make sense as to why it has higher occurrence during the puberty years when hormones are changing quite dramatically.
There are four main factors that contribute to acne: oil production, dead skin cells, clogged pores, and bacteria. It’s important to note that stress does not cause acne, but can worsen the condition. Furthermore, dirty skin does not lead to acne either, so it does not mean that someone who has acne doesn’t wash their face.
When hair follicles beneath the skin become clogged by oil, bacteria can thrive in such environment. Bacteria in these areas then lead to inflammation, which causes the bulge of a whitehead, blackhead, or pimple.
Factors that may worsen acne include changes in hormones, certain medications, diet, and stress. Some commonly believed factors like greasy food, dirty skin, and cosmetics do not contribute to acne.
Symptoms of acne include whiteheads, blackheads, small red tender bumps, large painful bumps beneath the skin, and painful pus-filled lumps underneath the skin.
Acne treatment
Treatment for acne can range from over-the-counter solutions to prescription medications depending on severity. Remedies for acne aim to dry out the oil and kill bacteria, and can come in the form of gels, creams, soaps, pads, or lotions. If over-the-counter products do not resolve your acne problem within two months, speak to your doctor about prescription medications.
Antibiotics, retinoid cream, birth control pills, and isotretinoin may be prescribed in severe cases of acne.
Otitis media (ear infection)
An ear infection commonly causes ear pain, but sometimes it can lead to a lump behind the ear. Ear infections are commonly seen in children and infants, but they can occur at any age. An ear infection may often occur after a cold or flu, or run along other respiratory infections.
Otitis media symptoms and causes
Ear infections are common in younger children because their Eustachian tube is much softer, meaning it has a harder time to stay open. Allergies, sinus infections, colds, and post-nasal drainage can all interfere with the Eustachian tube.
Signs and symptoms of otitis media include fever, pain, difficulty hearing, sore throat, neck pain, nasal congestion, headache, ringing in the ears. Children may cry, have difficulty sleeping, and pull at their ears.
Common risk factors for middle ear infection include a recent illness, history of allergies, exposure to secondhand smoke, pacifier use, and a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Otitis media treatment
Treatment for otitis involves treating the infection and relieving related symptoms, but generally ear infections will clear up on their own. One study found nearly two-third of children experience improvements in their condition within 24 hours. Antibiotics, along with over-the-counter pain relievers, can be used to treat ear infections.
Alternative methods to treat ear infections include herbal ear drops, application of a warm towelette to the area, and homeopathic remedies.
If middle ear infections are recurrent in a child, your doctor may advise to have drainage tubes put in to prevent the recurrence and to lower the risk of hearing-related complications.
As you can see, there is a variety of reasons for a person to develop a painful lump behind the ear, and although many of the causes are not life-threatening, you should still have your doctor look at the lump and determine the cause as the solution may be simpler than you think.