The study included 355 ischemic stroke patients over the age of 65, with 55 percent of them being men. The participants were enrolled in the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi (BASIC) Project. They were screened for sleep apnea using a portable respiratory monitor for about 13 days after a stroke.
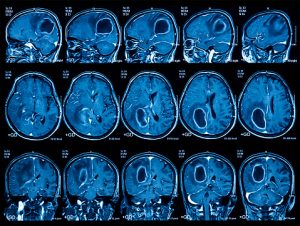
Neurologists also interpreted CT and MRI brain scans to determine whether the patients had brain stem involvement or no brain stem involvement. Of the 11 percent of participants who had a brain stem injury 84 percent had sleep apnea. Fifty-nine percent of participants without brain stem involvement had sleep apnea.
Dr. Brown added, “While these numbers are high, more research into the relationship between stroke and sleep apnea is needed before we recommend routine sleep apnea screening in post-stroke patients.”
Future research is set out to further explore the connection between sleep apnea and stroke.
Brain stem stroke diagnosis and treatment options
In a brain stem stroke, the blood flow to the brain stem stops or slows down, causing damage to the point where it can no longer function. Symptoms of a brain stem stroke include difficulty breathing and speaking, problems with chewing or swallowing, partial or complete hearing loss, blurred vision, weakness of the limbs, paralysis, and numbness or loss of sensation.
Diagnosis of a brain stem stroke must occur as soon as possible, because the longer a patient goes without a diagnosis and treatment the greater the risk is for complications and even death. A CT or MRI scan can be utilized in order to spot a brain stem stroke, but other tests may be ran as well, as brain stem strokes are often difficult to diagnose.
Treatment involves dissolving the blood clot first and foremost. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) drugs are used for this task as they are highly effective. To boost the effectiveness, tPA drugs should be given within the first three hours of the presence of stroke symptoms.
The type of brain stem stroke a patient has – ischemic or hemorrhagic –will also determine which other drugs and treatment methods need to be utilized.
Other post-stroke treatments include bladder retraining, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical rehabilitation – depending on what has become affected as a result of the stroke.
Related Reading:
Seasonal flu shot reduced influenza, swine flu, and stroke risk
The seasonal flu shot can help reduce the risk of influenza, swine flu, and even cut your risk of stroke. This year’s flu shot, in particular, has been shown to be the most effective in the last few years, with nearly a 60 percent effectiveness, according to reports from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Continue reading…
Stroke risk may increase with stress of caring for sick spouse, violence
Stroke risk may increase with caring for a sick spouse or experiencing violence. In a study, spouse caregivers that were stressed had a 95 percent higher risk of stroke, compared to matched controls. Continue reading…
Sources:
http://guidedoc.com/brain-stem-stroke-symptoms-prognosis-recovery