 One in four people worldwide will die as a result of a condition caused by deep vein thrombosis. Not sure what that is? In layman’s terms, it’s a blood clot. It can be a very serious and dangerous condition when not treated.
One in four people worldwide will die as a result of a condition caused by deep vein thrombosis. Not sure what that is? In layman’s terms, it’s a blood clot. It can be a very serious and dangerous condition when not treated.
Blood clots can lead to stroke, heart attack, or a life-threatening clot in the lungs or legs.
Advertisement
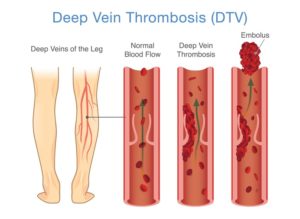
Blood clots are referred to differently depending on their location. When a clot is located deep in the leg, it is known as deep vein thrombosis. A clot that has moved with blood circulation and lodges in the lung is known as pulmonary embolism. Together, these conditions are referred to as venous thromboembolism and can be a very deadly combination.
Women may be at a heightened risk of blood clots during pregnancy, taking birth control pills, or during hormone replacement therapy.
A person may have a higher risk blood clots if they have a family history of them or because of genetic factors.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of blood clots is important due to the deadly risk many of them can bring with them.
Advertisement
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis include pain, tenderness, swelling, redness, discoloration, and warmth around the calf/thigh area. Pulmonary embolism may cause shortness of breath, rapid breathing, chest pains, rapid heart rate, and lightheadedness/passing out. If you experience these symptoms, you should seek medical treatment as quickly as possible.
You may reduce your risk of blood clots by regularly exercising, using blood thinners as prescribed, avoiding sitting or standing for prolonged periods of time, losing weight if you are overweight, staying well hydrated, and wearing loose-fitting clothing when traveling.
Also read:
- Rheumatoid arthritis increases deep vein thrombosis (blood clots in legs) and blood clot in lungs risk, study
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Vein Health
